Introduction
Since with the release 4.5 (1998), SAP had placed the Warehouse Management (LE-WM) module as a subcomponent under the Logistics Execution (LE) component where it was tightly integrated with the remaining two subcomponents such as Shipping (LE-SHP) and Transportation (LE-TRA).
With the advent of HANA data base technology (2010-11) and the advancement of SAP’s thought process to embark on S/4 HANA (2015-16), every ones’ minds are full of apprehensions about the future of Business Suite, especially ERP 6.0. While everybody is digesting the fact that the Warehouse Management (LE-WM) solution is waiting for the death on its ICU bed (Compatibility Pack with its expiry date in 2025), there is a twist with S/4 HANA 1909 release.
Let’s see what it is……!!!!
Can’t wait …? Click Curriculum to jump to course directly
WM reborn?
YES it is born again. During the early release of S/4 HANA, SAP thought that it could play smart to force all of its customers to embark on Extended Warehouse Management (EWM) solution by stopping the support for existing WM solution in S/4 HANA. Initially SAP declared that it is not going to support WM solution in S/4 HANA beyond 2025 (2270211-S4TWL – Warehouse Management (WM)) but later it shifted this deadline to 2027 and finally it realized that it can’t dare to trick it’s huge customer base anymore and declared that it will support basic functions of WM solution under the new brand name Stock Room Management with S/4 HANA 1909 release (Sep 2019).
It is really a big relief not only for enterprises which are using SAP WM since decades but also for SAP consultant who are supporting SAP WM solution.
WM lost its power?
NO not really. Though it looks like a big relief, there are certain limitations imposed by SAP along with its commitment to support WM solution beyond 2025. Significant number of customers may not get impacted because of these limitation but we need to wait to see what these limitations may mean to the real business world
WM is going to lose its power because Task & Resource Management (WM-TRM), Warehouse Control Unit interface (WM-LSR), Value Added Service (WM-VAS), Yard Management (WM-YM), Cross-Docking (WM-CD), Wave Management (WM-TFM-CP), and de-central WM (WM-DWM) are not part of Stock Room Management. SAP has provided a compliance check program (via the note 2882809 – Scope Compliance Check for Stock Room Management) to assess if the existing functionalities of WM are compliant to the scope defined for Stock Room Management.
What is still not clear is the integration between Transportation Management (SAP TM based on S/4HANA or SCM) and Stock Room Management. SAP made its decision firm on killing classic Transportation (LE-TRA) module which now waiting for its final nail in the coffin under compatibility pack in S/4 HANA (2270199 – S4TWL – Transportation (LE-TRA)). This means that Stock Room Management may not have bright future beyond 2027 unless SAP commits to extend integration between SAP TM and Stock Room Management.
WM still worthy?
YES it is still worthy. Though it’s not a comprehensive solution compared to EWM, it is still powerful because of its simplicity, stability and reliability. EWM still struggling to penetrate in to the market just because of the fact that the SAP WM can cater the needs of majority of customers’ needs. For sure Stock Room Management retains its significance at least until 2030 despite of its limitations.
Reference SAP Notes:
2881166 – FAQ : Stock Room Management
2270211 – S4TWL – Warehouse Management (WM)
2270199 – S4TWL – Transportation (LE-TRA)
2577428 – Road map for LE-WM in SAP S/4HANA
2882809 – Scope Compliance Check for Stock Room Management
2813859 – SAP S/4HANA 1909 Supply Chain for Transportation Management – Release information
Main Features of Warehouse/Stock Room Management
- Comprehensive inventory management
Unlike Inventory Management (MM-IM which is part of MM) which can only provide total quantity of material in stock, WM provides precise location for a specific quantity of a material and informs whether this this quantity is currently in a storage bin or in the transit.
- Mapping of all goods movements
All good movements such as receipts against purchase/production orders/ customer returns, issue against sales/production orders, transfer postings or posting changes, and physical inventory adjustments etc. are mapped to warehouse management processes. Processes can be mapped both with and without deliveries.
- Automatic bin determination
Using special operational document, Transfer Order, system determines the bins automatically for putaway during inbound operation and for picking during outbound operations. It also allows manual interventions for changing bins if required.
- Mobile data entry (MDE)
Comprehensive solution based on radio frequency (RF) technology to handle all most all warehouse floor operation such as inbound, outbound, packing, loading and inventory counting using a hand-held mobile devices (RF guns).
- Queue Management
Automatic grouping of warehouse activities in to queues and automatic assignment of queues to resources/operators. Queue monitoring dash board with drag and drop features to monitor and assign tasks to resources/operators.
- Monitoring & Error Handling
Warehouse Activity Monitor is the powerful to identify the failed transaction and correct them in a timely manner.
- Integration with external systems
Connection to specialist external systems such as Warehouse Control Unit (WCU) or Fork Lift Control Systems (FCS) using WMS-WCU an interface. (SAP is going to kill this feature in Stockroom Management after 2027)
Integration with other components of ERP
WM is tightly integrated with other application components via interfaces. Following components are connected with WM. No other components are integrated with WM but is possible to establish an indirect integration with Handling Unit Management (HUM) via Storage Unit Management.
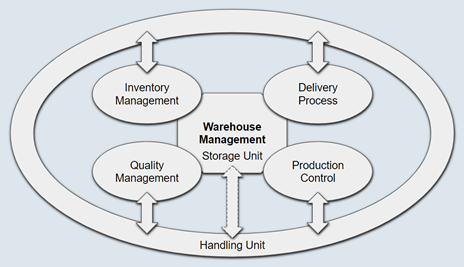
Integration with Inventory Management (IM) via movement type plays a significant role. Inventory postings either triggers a WM activity or completes an activity in receipts/issues processes.
Though it is not mandatory, integration with Delivery (LE-SHP) process makes WM process comprehensive and realistic especially in case of outbound process for sales.
Integration with Production (PP-PI) via production supply areas (PSA) gives an edge to automate component staging so that the materials can be staged to production shop floor without posting good issue material document.
If the Quality Management (QM) is implemented then the WM process can be integrated, of course it is not very comprehensive, to control how goods are dealt with in the warehouse if they are subjected to quality inspection.
Last but not the least, the indirect integration with Handling Unit Management (HUM) via Storage Unit Management (SUM) enables the re-use of the barcode label printed by vendors for further movement in the warehouse.
Curriculum
Let’s get started with the curriculum. What all you need to do is just follow the topics in the prescribed sequence based on your relevance to the topic.
| S.No. | Topic | Relevance* | Certification |
| 01 | Logistics Execution (LE) – Overview | BU-JC | Yes |
| 02 | Warehouse Structure | BU-JC | Yes |
| 03 | Integration between IM and WM | JC | Yes |
| 04 | Interim storage type and its determination | JC | Yes |
| 05 | Warehouse Documents | BU-JC | Yes |

